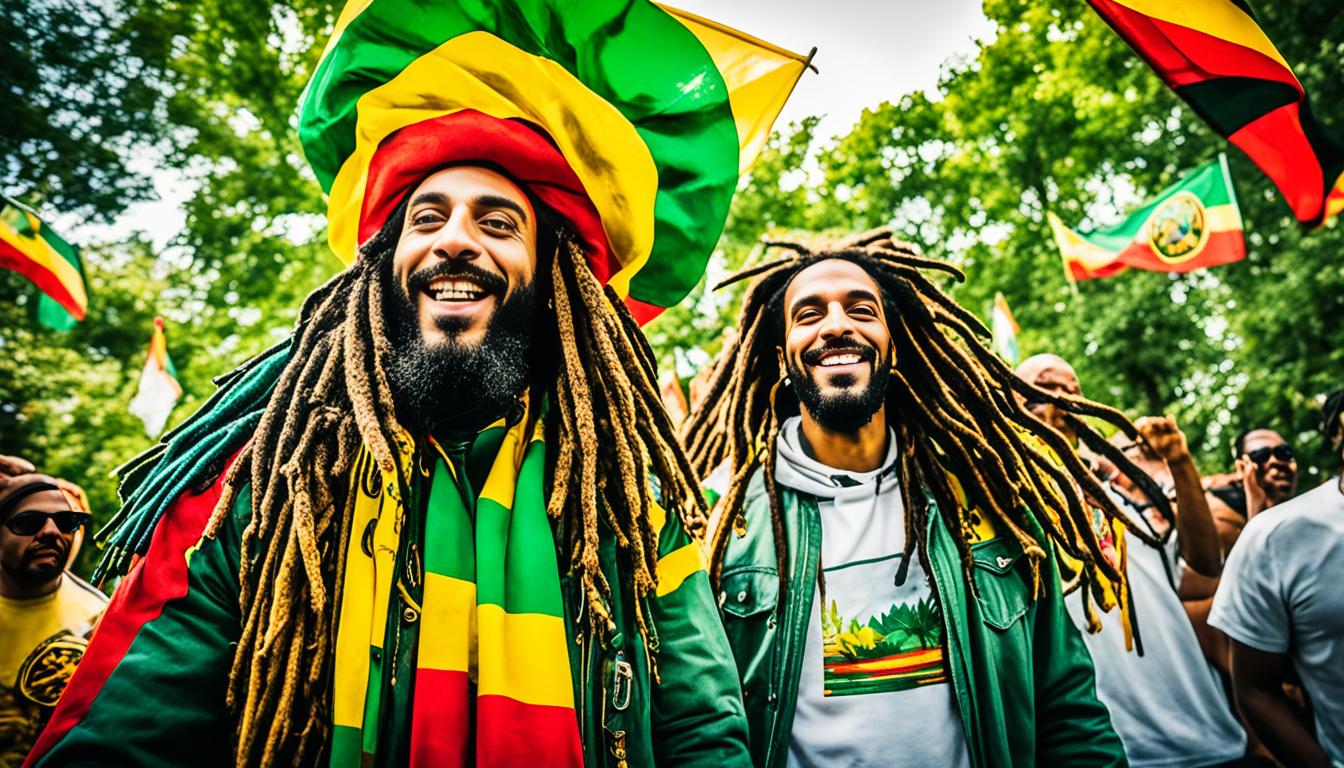
The Rastafari movement, with its profound cultural and spiritual foundations, emerged in Jamaica in the 1930s. Marcus Garvey’s prophecy, predicting the crowning of a black king in Africa who would act as a redeemer, ignited this movement. When Haile Selassie I ascended to the Ethiopian throne, many Jamaicans perceived this event as the realisation of Garvey’s vision. Selassie is often regarded as the Black Messiah, also known as Jah Rastafari. The movement’s origins are deeply interwoven with the response to oppression and a reclamation of African heritage.
Beyond its religious label, Rastafari is a holistic Indigenous movement encompassing social and political aspects, with a commitment to justice, empowerment, and harmony with nature. Recently, Rastafari culture has been increasingly acknowledged and accepted globally. The focus on natural ingredients, adhering to a lifestyle free from conventional societal norms, and an anti-establishment ethos are crucial elements of Rastafari beliefs. These elements underscore the movement’s essence beyond the usual associations with marijuana, reggae music icons like Bob Marley, and the distinctive dreadlocks.
The unique combination of spirituality, cultural pride, and advocacy for natural living has made the rastafarian movement resonate with people worldwide, transcending its Jamaican origins to become a global phenomenon.
Key Takeaways
- The Rastafari movement originated in Jamaica in the 1930s.
- Marcus Garvey prophesied the rise of a black king, who was later identified as Haile Selassie I.
- Rastafari extends beyond religion, encompassing social and political dimensions.
- The movement stresses natural living and a lifestyle diverging from conventional societal norms.
- Global recognition has been spurred by icons like Bob Marley and the movement’s cultural practices.
- The roots of rastafarian beliefs lie in addressing oppression and rediscovering African heritage.
The Origins of Rastafari
The inception of the Rastafari movement is deeply intertwined with the ideals and visions set forth by Marcus Garvey. His impact on black empowerment and African heritage fostered a pivotal juncture for many individuals in Jamaica, seeking a form of spiritual and cultural identity.

Influence of Marcus Garvey
Marcus Garvey, a prominent Jamaican black political leader, fervently advocated for black pride and a return to African roots. His teachings became a cornerstone for many within the Rastafari movement. Garvey’s powerful speeches and writings evoked a sense of unity and resilience among the Jamaican people.
Prophecy and the Crowning of Haile Selassie
A fundamental aspect of Garvey’s influence was his visionary prophecy which predicted the crowning of a black king in Africa, perceived as a redeemer. This prophecy found its culmination in the haile selassie crowning in Ethiopia, where Selassie assumed titles resonating with biblical significance. Many Jamaicans interpreted this event as the realisation of Garvey’s prophecy, heralding Selassie as the black messiah, also revered as jah rastafari.
This perceived fulfilment forged a profound spiritual and cultural movement, embedding the prophecy and the significance of Haile Selassie within the core of Rastafari beliefs.
Beliefs and Practices of the Rastafari Movement
The Rastafari movement is distinguished by its unique doctrines and customs that draw from a blend of religious, social, and cultural elements. Central to the rastafari faith is the recognition of Haile Selassie as the living God and the symbolic representation of the Lion of Judah, embodying strength and resistance.

Central Tenets and Faith
Among the foundational rastafari tenets, the view of Ethiopia as Zion – a promised paradise – is paramount. This belief underscores the movement’s emphasis on a spiritual homeland, distinct from the physical confines of Babylon, symbolising oppression and exile. The philosophy of Rastafari encompasses notions of self-reliance, communal living, and an immutable connection with nature.
Importance of Natural Lifestyle
A pivotal aspect of the philosophy of rastafari is the commitment to a natural lifestyle, often referred to as ‘livity.’ This principle encourages adherents to harmonise with the Earth and adhere to an ital diet, which primarily consists of natural, organic, and unprocessed foods. The ital diet excludes meat, advocating for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and grains to sustain both the body and the spirit. This dedication to natural living reflects the broader Rastafari ethos of purity, sustainability, and holistic well-being.
Haile Selassie: The Black Messiah
Haile Selassie holds a pivotal place in the Rastafari movement, symbolising the fulfilment of biblical prophecies and embodying the hopes of many as the Rastafari messiah.

His Significance and Titles
The titles bestowed upon Haile Selassie, such as ‘King of Kings’ and ‘Lord of Lords’, underscore the significance he held within the Rastafari faith. These grandiose titles were seen as a clear indication of his elevated status, not just politically, but spiritually as well. He was hailed as the Black Messiah, affirming his divine role in the context of Rastafari beliefs.
Connection to Biblical Prophecies
Haile Selassie’s lineage, which is claimed to trace back to King David, provides a profound connection to biblical prophecies. This link reinforced his image as the Rastafari messiah, fulfilling the divine expectations set forth in scriptures. Consequently, his rise to the throne was viewed as a historic and spiritual milestone, solidifying his place as the cornerstone of the Rastafari movement.
The Role of Reggae Music
Reggae music has been instrumental in disseminating the messages of Rastafari culture to a global audience. This powerful genre, characterised by its syncopated rhythms and profound lyrics, has served as a conduit for expressing the struggles, resilience, and spirituality of the Rastafari people.

Bob Marley and Global Recognition
Among the many artists who have embraced and propagated reggae music, Bob Marley stands as the most iconic figure. His music transcended borders, providing a voice to the oppressed and shedding light on the socio-political issues pertinent to Rastafari global recognition. Through Marley’s dedication and evocative compositions, such as “One Love” and “Redemption Song”, the tenets of Rastafari culture were brought to the forefront of global consciousness. Marley’s legacy continues to inspire and educate new generations about the values of unity, peace, and justice inherent in the Rastafari movement.
Influence of Reggae on Rastafari Popularity
The impact of reggae music on the rise in popularity of the Rastafari movement cannot be overstated. By embedding the philosophical and spiritual elements of Rastafari within their lyrics, reggae artists have effectively used their music as a medium for advocacy and education. The music of Rastafari, with its rich cultural narrative, has played a pivotal role in bringing attention to the plight and aspirations of the Rastafari community. This genre has not only achieved widespread acclaim but also facilitated a greater understanding and appreciation of Rastafari culture, making it an indelible part of the global musical landscape.
The Symbolism of Dreadlocks
Dreadlocks stand as one of the most recognisable elements of Rastafari appearance, intertwining deeply with various cultural, spiritual, and historical narratives. Often perceived merely as a hairstyle, the symbolism of dreadlocks delves into the realms of African heritage, Rastafari identity, and spiritual beliefs.

Historical Background
The origins of dreadlocks date back to ancient African civilisations, where natural hair was styled into locks as a sign of strength and spiritual energy. The aesthetics of this hairstyle have traversed through time, representing a deep-rooted connection between individuals and their African heritage. For Rastafarians, this practice signifies a return to naturalism and a rejection of Western beauty standards.
Cultural and Spiritual Significance
In Rastafari culture, dreadlocks hold profound spiritual significance. They emulate the mane of a lion, an animal revered for its power and wisdom, symbolising the strength and pride of the Rastafari community. The act of locking hair is not merely a tradition but a manifestation of Rastafari identity. Embracing dreadlocks affirms one’s faith, symbolises a vow of separation from Babylon (oppressive Western society), and signals an unwavering connection with the divine.
Thus, the significance of dreadlocks transcends aesthetic value, embodying the unyielding spirit of the Rastafari movement. Through this tradition, the Rastafari appearance continually commemorates the everlasting bond with their ancestors and spiritual journey.
The Importance of Ganja in Rastafari Culture
Ganja, known globally as marijuana, holds a revered place in Rastafari culture. Unlike its recreational use elsewhere, within Rastafari it is a sacred tool intended to enhance meditation and the process of reasoning. This profound spiritual use of ganja is deeply rooted in the belief that the herb facilitates a closer connection to the divine. Rastafari adherents consider ganja a sacred gift that aids in spiritual enlightenment and communal bonding.
Spiritual and Ritualistic Use
The ritualistic use of marijuana, or ganja, in Rastafari ceremonies includes its presence in reasoning sessions where members come together to discuss and contemplate spiritual themes. This practice is seen as a sacred rite, uplifting the mind and spirit. By invoking a state of heightened consciousness, the spiritual use of ganja helps Rastas seek truth and enlightenment, bringing them closer to Jah, their God.
Legal Struggles and Perceptions
Legal struggles surrounding ganja have been a significant issue for Rastafari communities. Despite its importance in spiritual rituals, the global legal framework tends to criminalise marijuana, challenging Rastafari practices. Numerous ganja legal struggles involve the community’s fight for religious exemption, advocating for the recognition of their right to use ganja as an integral part of their faith. These legal battles highlight the differing perceptions of ganja, from a sacred substance in Rastafari culture to a prohibited drug in many jurisdictions.
As these perceptions evolve, the pursuit for acceptance of ganja’s spiritual significance continues, emphasising its irreplaceable role in ritualistic use within Rastafari. This dynamic underscores the ongoing tension between religious practices and legal constraints, a complex interplay that will likely shape future discourse on the spiritual use of ganja.
The Ital Lifestyle
The Ital lifestyle is a fundamental aspect of Rastafari culture, promoting a harmonious connection with nature through a diet that emphasises purity and vitality. This approach to living extends beyond food, encompassing a broader philosophy of natural living and organic principles, which aligns spiritual well-being with physical health.
Principles of Natural and Organic Living
The principles behind the Ital lifestyle are deeply rooted in the belief that natural living fosters a better connection with the earth. The tenets advocate for the consumption of organic principles ingredients, as these are believed to be free from pollutants and toxins. Beyond dietary choices, adherents of the Ital lifestyle also seek out natural materials and sustainable practices in their daily lives, reinforcing the symbiotic relationship between humanity and the environment.
Rastas believe that living naturally and organically increases one’s ‘livity’, a term they use to describe an elevated state of living in harmony with the universe.
Common Foods and Diet Practices
Foods embraced in the Rastafari diet include a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, often sourced locally and grown without synthetic chemicals. The diet is primarily plant-based, avoiding meat and processed foods, which are seen as impurities. Important staples of Rastafari cuisine include foods like yam, callaloo, ackee, and coconut. These ingredients are not only nutritionally rich but are also prepared in a way that retains their natural goodness, further embodying the Ital lifestyle.
Adopting this cuisine is seen as a means of purifying both the body and the soul, reinforcing the connection between diet, health, and spiritual livelihood. The Rastafari diet is thus not merely a set of eating habits but a holistic approach to natural living that influences every aspect of life.
Rastafari in Jamaica
The Rastafari movement has deep historical roots in Jamaica, and its development has profoundly influenced Jamaican culture. Initially, Rastafari was a response to social and political oppression, serving as an anchor for those seeking a connection to their African heritage. The movement began in the 1930s and has since grown, evolving in response to changing times while remaining true to its foundational principles.
Historical Roots and Development
The historical roots of Rastafari in Jamaica can be traced back to the teachings of Marcus Garvey and the crowning of Haile Selassie I. As a movement, Rastafari’s development has mirrored the struggles and triumphs of the Jamaican people. The emphasis on African identity and cultural re-appropriation was a key element, giving the movement a solid grounding in addressing the injustices experienced by the African diaspora. Over the decades, Rastafari has grown from a relatively small group to a globally recognised movement, influencing not just religion but also art, music, and politics in Jamaica.
Modern Day Practices and Communities
Today, modern Rastafari communities in Jamaica continue to thrive, embracing both traditional practices and contemporary developments. Rastafari development includes a commitment to social justice, environmental sustainability, and a natural way of life. From urban centres to rural enclaves, these communities embody the spirit of unity and freedom that the movement stands for. The Jamaican culture has been significantly enriched by the contributions of Rastafari, cementing its place as a vital component of the nation’s identity.
The lasting influence of Rastafari in Jamaica cannot be overstated. Its principles have been woven into the fabric of Jamaican culture, impacting everything from religious beliefs to day-to-day lifestyles. As the movement continues to evolve, it remains a cornerstone of cultural and spiritual life in Jamaica, offering a unique perspective on justice, empowerment, and connection to nature.
Ethiopia: The Promised Land
Rastafarians revere Ethiopia as the biblical Zion, symbolising a spiritual haven and a land of prophetic redemption. Often referred to as the Promised Land, it represents hope, repatriation, and liberation from oppression. This holy land is more than a geographical entity; it is a beacon of the Rastafari aspiration for a return to ancestral roots and a reclaiming of African heritage.
Significance of Zion within Rastafari
The term ‘Zion’ in Rastafari lexicon transcends physical dimensions, embodying a spiritual paradise where Rastas achieve unity with Haile Selassie, whom they regard as a divine figure. For many Rastafarians, Ethiopia embodies this Zion, a sanctuary where they can escape the ‘Babylon’ of Western oppression and connect deeply with their faith. The significance of Zion serves as a fundamental pillar in Rastafari beliefs, constantly reinforcing their commitment to cultural and spiritual rejuvenation.
Historical Ties to Ethiopia
The historical ties between Ethiopia and Rastafari are profound and multifaceted. The crowning of Emperor Haile Selassie I in 1930 played a pivotal role in the movement, fulfilling Marcus Garvey’s prophecy of a black king. This event cemented Ethiopia’s status as a sacred land within Rastafari thought. Additionally, Ethiopia’s ancient Christian heritage and its resistance to colonialism have fortified its esteem, making it a symbol of strong African sovereignty and spiritual sanctity. The country’s rich history and enduring legacy continue to inspire Rastafari Zionism and the global quest for racial and cultural identity.
FAQ
What are the origins of the Rastafari movement?
How did Marcus Garvey influence the Rastafari movement?
What are the central beliefs and practices of Rastafarianism?
Why is Haile Selassie referred to as the Black Messiah?
How has reggae music influenced the Rastafari movement?
What is the significance of dreadlocks in Rastafari culture?
Why is ganja important in Rastafarian rituals?
What does the Ital lifestyle entail?
How has Rastafari evolved in Jamaica?
What is the role of Ethiopia in Rastafari belief?
In “Black Pearls: A Celebration of Legendary Black Women in the United Kingdom,” prepare to be inspired by the extraordinary stories of resilient and brilliant Black women who have shaped British history. This powerful book sheds light on the often overlooked contributions and achievements of these remarkable individuals, showcasing their resilience and determination in the face of immense challenges. From breaking barriers to redefining narratives, these women have left an indelible mark on British society, and their stories will leave you in awe of their strength and tenacity.