When it comes to breast cancer, one question that many people ask is whether it is hereditary. The answer is that some cases of breast cancer do have a genetic component. Understanding the role of genetics in breast cancer can help individuals make informed decisions about prevention, screening, and treatment.
Researchers have identified a number of gene mutations that increase the risk of developing breast cancer. The most well-known of these are mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. When these genes are altered, they can no longer function properly, leading to an increased risk of cancer.
While genetic factors play a role in breast cancer, it’s important to note that not all cases of breast cancer are hereditary. In fact, the majority of cases are thought to be caused by a combination of lifestyle, environmental, and hormonal factors.
In this article, we’ll explore the role of genetics in breast cancer and discuss the significance of family history in determining risk. We’ll also cover options for genetic testing, prevention and early detection strategies, and available treatment options.

Key Takeaways:
- Breast cancer can have a genetic component, but not all cases are hereditary.
- Gene mutations, such as those in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, can increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
- Family history is important in assessing risk, but lifestyle and environmental factors also play a significant role.
- Genetic testing can help individuals identify their risk of hereditary breast cancer.
- Prevention strategies, early detection, and treatment options are available for individuals at risk of developing breast cancer.
Understanding Genetic Factors in Breast Cancer
When it comes to breast cancer, genetic factors can play a crucial role in determining an individual’s risk of developing the disease. While most cases of breast cancer are not hereditary, some are caused by mutations in certain genes that increase susceptibility.
The most well-known of these gene mutations are in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are responsible for producing proteins that help to prevent the growth of tumours. Women who have inherited mutations in one of these genes are at a significantly higher risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer compared to the general population.
Research has shown that these mutations are responsible for around 5-10% of all breast cancer cases.
The Importance of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can be a valuable tool in assessing an individual’s risk of developing hereditary breast cancer. The test involves analysing a sample of blood or saliva to look for specific mutations in genes that are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
It’s important to note that genetic testing is not recommended for everyone. Rather, it is typically offered to individuals with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, particularly if multiple relatives have been diagnosed at a young age.
If a mutation is identified, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their risk, such as increased surveillance or preventative surgery.
Other Genetic Risk Factors
While BRCA mutations are the most well-known genetic risk factors for breast cancer, there are other gene mutations that have been associated with an increased susceptibility to the disease. For example, mutations in the TP53 gene have been linked to Li-Fraumeni syndrome, which is characterized by a high risk of multiple types of cancer, including breast cancer.
Some studies have also suggested that variations in certain other genes, such as CHEK2 or ATM, may be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, particularly in individuals with a family history of the disease.
Familial Breast Cancer: Exploring Family History
In this section, we’ll focus on familial breast cancer, which refers to cases where multiple family members have been diagnosed with the disease. It is essential to understand the significance of family history in determining the risk of developing breast cancer.
According to the National Breast Cancer Foundation, a woman’s risk of developing breast cancer nearly doubles if she has a first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter) who has been diagnosed with the disease. Additionally, women with a family history of breast cancer are at a higher risk of developing cancer in both breasts.
It’s important to note that having a family history of breast cancer doesn’t necessarily mean you will develop the disease. However, it may increase your risk, and therefore, you should take proactive steps to manage your risk factors.
Risk Factors for Familial Breast Cancer
Various risk factors may contribute to the development of familial breast cancer, including:
- A family member diagnosed with breast cancer before the age of 50
- Multiple family members diagnosed with breast and/or ovarian cancer
- Male family members diagnosed with breast cancer
- Family members with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation
If you have a family history of breast cancer that meets any of the above criteria, you may have an increased risk of developing the disease. It’s essential to speak to your doctor and discuss appropriate screening and prevention strategies.
Importance of Screening and Early Detection
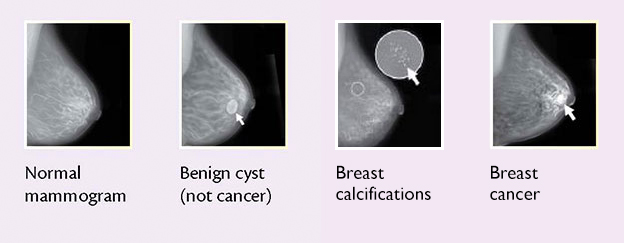
If you have a family history of breast cancer, your doctor may recommend starting mammograms earlier than the recommended age of 50. Regular mammograms, along with clinical breast exams and self-exams, can help detect breast cancer early, when it’s most treatable.
If you notice any changes in your breasts, such as a lump or skin changes, make sure to contact your doctor immediately. Early detection is key in improving outcomes and increasing chances of survival.
Next, we’ll delve deeper into inherited breast cancer, where specific gene mutations are passed down through generations.

Individuals with a family history of breast and ovarian cancer should consider genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Additionally, certain ethnic groups, including Ashkenazi Jews, have a higher prevalence of these mutations.
Other risk factors for hereditary breast cancer include a personal history of breast cancer, a history of radiation therapy to the chest, and certain benign breast conditions.
If you have a BRCA gene mutation, there are several options available to manage your risk of developing breast cancer. These may include increased surveillance with regular mammograms and breast MRIs, chemoprevention with drugs such as tamoxifen, or risk-reducing surgery such as a prophylactic mastectomy or oophorectomy.
Lifestyle Factors and Their Influence on Breast Cancer
While genetics play a significant role in determining the risk of developing breast cancer, lifestyle factors can also impact the likelihood of developing the disease. In fact, studies suggest that up to one-third of breast cancer cases may be preventable through lifestyle choices.
Breast Cancer Risk Factors
There are several lifestyle factors that can increase the risk of developing breast cancer, including:
- Obesity or being overweight
- Lack of physical activity
- Alcohol consumption
- Smoking
- Exposure to environmental toxins
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
It is important to note that these risk factors can have a greater impact on individuals with a genetic predisposition to breast cancer. For example, women with a BRCA gene mutation who are also overweight have been shown to have a higher risk of developing breast cancer than those without the mutation.
The Role of Exercise
Regular physical activity has been linked to a decreased risk of breast cancer. The NHS recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling.
A study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute found that vigorous exercise, such as running or fast-paced cycling, was particularly effective at reducing the risk of breast cancer in premenopausal women.

Diet and Nutrition
Eating a healthy and balanced diet can also help reduce the risk of breast cancer. This includes limiting the consumption of processed and high-fat foods and increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Some studies have also suggested that certain foods and drinks, such as cruciferous vegetables (e.g. broccoli, cauliflower), soy products, and green tea, may have a protective effect against breast cancer.
Reducing Breast Cancer Risk
By making lifestyle modifications, individuals can reduce their risk of developing breast cancer. This includes:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Staying physically active
- Limited alcohol consumption or abstaining from alcohol altogether
- Avoiding tobacco products and exposure to environmental toxins
- Choosing a healthy and balanced diet
It is also important for individuals with a family history of breast cancer to discuss their risk and appropriate screening guidelines with their healthcare provider.
Reducing Risk: Prevention and Early Detection Strategies
While certain factors, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, there are steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing breast cancer. Implementing a healthy lifestyle and adhering to regular screening guidelines are essential in prevention and early detection of breast cancer.

Breast Cancer Prevention
Implementing healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce the risk of developing breast cancer. Obesity, physical inactivity, and alcohol consumption are all factors that have been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. On the other hand, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and limiting alcohol intake can help to lower the risk of developing the disease.
Additionally, avoiding hormone replacement therapy, or only taking it for the shortest time possible under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can help to reduce the risk of breast cancer.
Early Detection of Breast Cancer
Early detection of breast cancer is crucial in improving treatment outcomes. The recommended screening guidelines for breast cancer include mammograms every 1-2 years for women over the age of 50 or those at high risk due to genetics or family history, and clinical breast exams every 3 years for women in their 20s and 30s and annually for women over 40.
It is important to note that individuals with a family history of breast cancer or those who have tested positive for certain gene mutations may be advised to start screening earlier or to undergo additional screening methods, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
As the famous saying goes, “prevention is better than cure.” By implementing healthy lifestyle habits and adhering to regular screening guidelines, individuals can take proactive steps in reducing their risk of developing breast cancer and improving their chances of early detection and successful treatment.
Managing Hereditary Breast Cancer: Treatment Options and Support
Being diagnosed with hereditary breast cancer can be a difficult and overwhelming experience. However, there are many treatment options available to manage the disease and support available to help individuals and their families through the process.
Treatment Options
The treatment options for hereditary breast cancer may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy. The most appropriate treatment plan will depend on the individual’s unique circumstances, including the stage and type of cancer, as well as their overall health status.
In many cases, surgery is the preferred treatment option. This may involve a lumpectomy or a mastectomy, depending on the extent and location of the cancer. For individuals with a higher risk of developing breast cancer due to genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, a prophylactic mastectomy may also be recommended as a preventative measure.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery to help shrink the tumour, kill any remaining cancer cells, and reduce the risk of recurrence. Targeted therapy, which involves medications that specifically target the cancer cells, may also be used in some cases.
Support for Breast Cancer Patients
Dealing with a breast cancer diagnosis can be emotionally and mentally challenging. Support is available for individuals and their families to help them navigate this difficult time. Support may include counselling, support groups, and access to other resources, such as financial assistance and transportation services.
Patients may also benefit from complementary therapies, such as massage therapy, acupuncture, and meditation, to help manage symptoms and improve their overall well-being. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and getting enough rest and sleep may also be helpful in managing the disease.
Genetic Counselling: Expert Guidance for Decision-Making
Genetic counselling is a process that helps individuals at risk of hereditary breast cancer make informed decisions about their health. It involves an in-depth analysis of the individual’s family history, genetic testing options, and the potential impact of any identified gene mutations. Genetic counselling can be particularly helpful for individuals who have a family history of breast cancer and are considering genetic testing.
During genetic counselling, a genetic counsellor will provide information about the risks and benefits of genetic testing and the potential implications of any test results. They will also discuss potential prevention and management strategies, such as increased surveillance or prophylactic surgery, and the emotional impact of a hereditary cancer diagnosis.
Deciding whether to undergo genetic testing for breast cancer can be a difficult decision, and genetic counselling can provide the necessary support and guidance to make an informed choice. It can help individuals understand their risk, weigh their options, and make decisions that are right for them and their families.
How Does Genetic Counselling Work?
Genetic counselling typically involves several sessions with a trained genetic counsellor who will review the individual’s medical and family history and discuss the potential risks and benefits of genetic testing. The counsellor will also help the individual understand the testing process and what the results might mean for their health and their families.
Genetic counselling may also involve discussing options for managing a hereditary cancer diagnosis, such as increased surveillance, prophylactic surgery, or targeted therapy. The counsellor can also provide emotional support and connect individuals with resources and support groups to help them cope with the impact of a cancer diagnosis.
The Benefits of Genetic Counselling
The benefits of genetic counselling for breast cancer are significant. By understanding their risk, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce their risk of developing breast cancer. Genetic counselling can also provide emotional support and resources for individuals and their families, helping them navigate the complex decisions involved in managing a hereditary cancer diagnosis.
Ultimately, genetic counselling empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health based on their unique circumstances and risk factors. It provides a roadmap for managing hereditary breast cancer and helps individuals take control of their health journey.
“Genetic counselling can provide the necessary support and guidance to make an informed choice. It can help individuals understand their risk, weigh their options, and make decisions that are right for them and their families.”
Empowering Yourself: Advocacy and Awareness
Advocacy and awareness are crucial in the fight against breast cancer. By spreading knowledge and supporting those affected by the disease, we can work towards better outcomes and a brighter future for all. Here are some ways to get involved:
Joining a Breast Cancer Advocacy Group
There are many organisations in the UK working towards breast cancer advocacy, such as Breast Cancer Now and Breast Cancer Care. By joining a group or becoming a volunteer, you can make a real impact in raising awareness and supporting those affected by the disease.
Raising Awareness
Spread the word about breast cancer by sharing information with friends and family. You can also participate in community events or fundraisers, such as charity walks, to help raise awareness and funds for research.
Self-Advocacy
By taking control of your own health and staying informed, you can become an advocate for yourself and others. Make sure to attend regular screenings and check-ups, and speak up if you notice any changes in your body.
Together, we can make a difference in the fight against breast cancer. By advocating for ourselves and supporting others, we can work towards a world where breast cancer is no longer a leading cause of death.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring the question of whether breast cancer is hereditary has highlighted the significance of genetic factors and family history in determining an individual’s risk of developing the disease. The knowledge gained about inherited and familial breast cancer emphasizes the need for genetic testing and counselling to empower individuals in making informed decisions regarding their health.
Prevention and early detection strategies, including lifestyle modifications and regular screening, remain vital in managing the risk of breast cancer, regardless of whether it is hereditary or not. For those diagnosed with hereditary breast cancer, access to treatment options and emotional support is crucial in navigating the challenging journey.
Genetic Counselling and Advocacy:
Expert guidance through genetic counselling and support from advocacy organizations and resources are essential tools for individuals and families affected by hereditary breast cancer. By staying informed and aware, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their risk and improve outcomes.
Overall, unpacking the truth about breast cancer heredity is an ongoing process, and continued education and awareness are critical components in the fight against breast cancer. By working together and supporting each other, we can make strides in reducing the impact of this disease.
FAQ
Is breast cancer hereditary?
Breast cancer can be hereditary, with certain genetic factors playing a role in its development. However, not all cases of breast cancer are hereditary, and lifestyle factors also contribute to the risk.
What are the genetic factors in breast cancer?
Genetic factors in breast cancer include gene mutations, such as BRCA gene mutations, which can increase the risk of developing the disease. Genetic testing can help identify these mutations.
How does family history affect breast cancer risk?
Family history is a significant factor in determining the hereditary nature of breast cancer. Having multiple family members diagnosed with the disease can increase an individual’s risk.
What is inherited breast cancer?
Inherited breast cancer occurs when specific gene mutations are passed down through generations. Genetic counselling and testing play a crucial role in identifying and managing the risk associated with these gene mutations.
What is genetic testing for breast cancer?
Genetic testing involves analysing a person’s DNA to identify gene mutations associated with an increased risk of developing breast cancer. It can help individuals understand their risk and make informed decisions about prevention and treatment.
What are BRCA gene mutations?
BRCA gene mutations are the most well-known genetic risk factors for hereditary breast cancer. These mutations increase an individual’s risk of developing both breast and ovarian cancer.
How do lifestyle factors influence breast cancer risk?
Lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical activity, alcohol consumption, and hormone replacement therapy can impact the risk of developing breast cancer, even in individuals with a genetic predisposition.
What are strategies for reducing the risk of breast cancer?
Strategies for reducing the risk of breast cancer include adopting a healthy lifestyle, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol consumption, and following recommended screening guidelines for early detection.
What treatment options are available for hereditary breast cancer?
Treatment options for hereditary breast cancer may include surgical interventions, targeted therapies, and emotional support and resources for individuals and their families.
What is genetic counselling for breast cancer?
Genetic counselling provides expert guidance to individuals at risk of hereditary breast cancer. It helps them make informed decisions about prevention, screening, and treatment by assessing their genetic risk and offering support throughout the decision-making process.
How can advocacy and awareness help in the fight against breast cancer?
Advocacy and awareness initiatives play a crucial role in supporting individuals affected by hereditary breast cancer. They offer resources, education, and support to empower individuals and promote a better understanding of the disease.
What is the conclusion regarding breast cancer heredity?
In conclusion, breast cancer can be hereditary, with genetic factors and family history playing a role in its development. However, lifestyle factors also contribute to the risk. By staying informed, undergoing genetic testing and counselling, and taking proactive steps, individuals can manage their risk and empower themselves in their health journey.